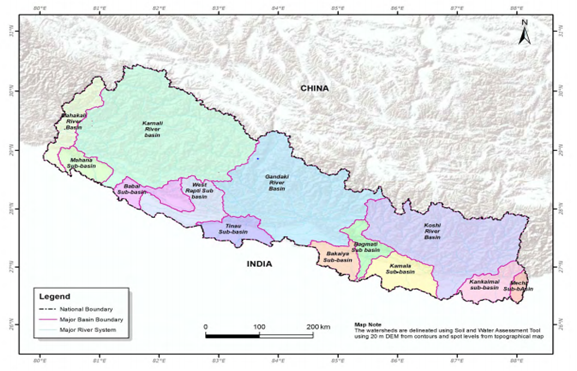
A river basin is any area of land where precipitation collects and drains off into a river and its tributaries. The river basin includes all the surface water from rain runoff, snowmelt, hail, sleet, and nearby streams that run downslope towards the shared outlet, as well as the groundwater underneath the earth's surface. Drainage basins connect into other drainage basins at lower elevations in a hierarchical pattern, with smaller sub-drainage basins, which in turn drain into another common outlet. River basins are typically made up of multiple watersheds.
River basin planning is the process by which decisions are made over the competing uses and different demands for water resources and associated systems within a basin. Basin plans set objectives and the measures for developing, protecting, and harnessing the resources of the basin in order to achieve these objectives and the health and safety of the river itself. In its most developed form basin planning can bring together a range of different disciplines and themes, from hydrology and engineering to ecology and economics. Basin planning has been undertaken over many years, for many different purposes and in different types of basins in many countries. Some of this planning has been very formal and organized; on other occasions, it is more sporadic, less organized, or develops organically over time. By nature, basin planning must reflect, consider and respond to the historical, physical, political, social, economic, and institutional characteristics of the basin and country.
River basin planning is of great importance for Nepal as many people directly depend on natural resources and river basins for their livelihoods. The Government of Nepal along with international and national organizations have been collaboratively working for the development of a comprehensive framework on river basin management across all levels of government.
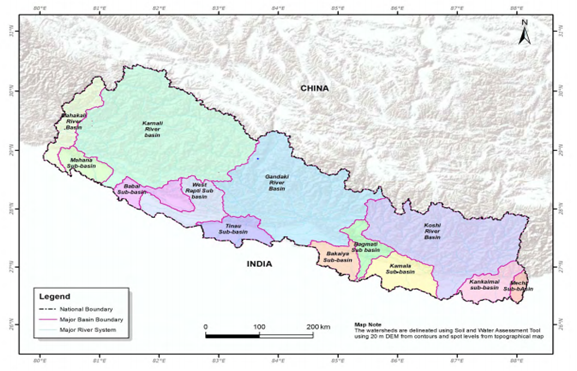
Figure 1 Major river basins of Nepal
